Botflies, scientifically known as Oestridae, are an intriguing but discomforting group of insects that have earned notoriety for their parasitic habits. These flies can be found across the globe and are distinct from other insects due to their peculiar reproductive strategy. Unlike many insects that lay their eggs directly on a host, female botflies take a different approach. They deposit their eggs on the skin or hair of various hosts, including livestock, pets, and even humans in rare cases. The trigger for egg hatching is the warmth of the host’s body, and once hatched, the tiny larvae burrow into the skin to begin their development.
The life cycle of botflies unfolds in four stages: eggs, larvae, pupae, and adults. Female botflies expertly attach their eggs to the host’s fur or skin. When the host’s body heat triggers hatching, small larvae emerge and swiftly seek shelter beneath the skin. Within the host, these larvae create a small opening for breathing and feed on tissue fluids, causing discomfort to the host due to their presence beneath the skin.
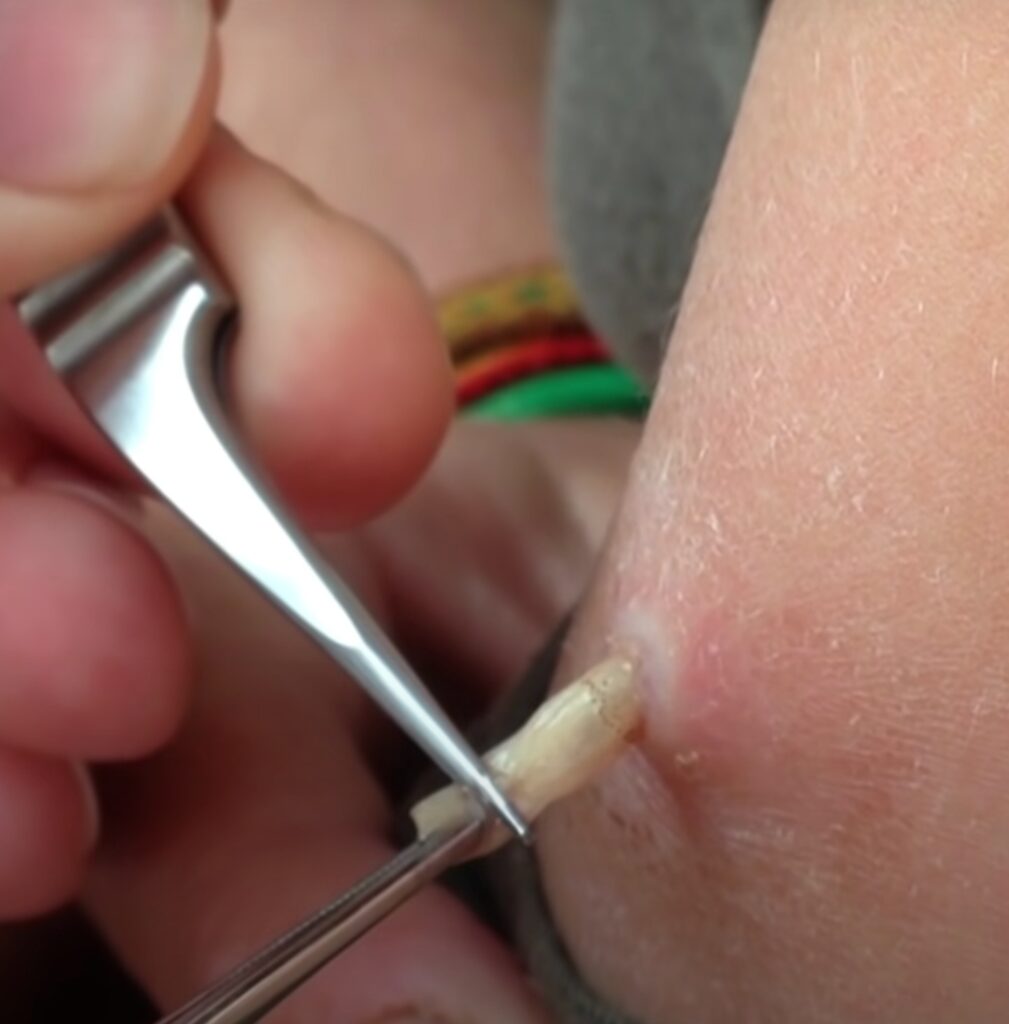
After several weeks of development, the mature larvae exit the host’s skin and fall to the ground to pupate. The pupal stage is a period of rest during which the larva transforms into an adult botfly. Once this transition is complete, adult botflies emerge from the pupal stage, and their focus shifts to reproduction, perpetuating the cycle as females lay their eggs on suitable hosts.
Dealing with botfly larvae can be unpleasant and even hazardous in some cases. Several removal methods exist, including surgical extraction, suffocation techniques using petroleum jelly or adhesive tape, and natural expulsion, where the body may eject the larva on its own, albeit slowly. Veterinary assistance is often necessary for pets and cattle infested with botfly larvae, involving techniques similar to surgical extraction and the prescription of medications to alleviate pain and prevent infection.
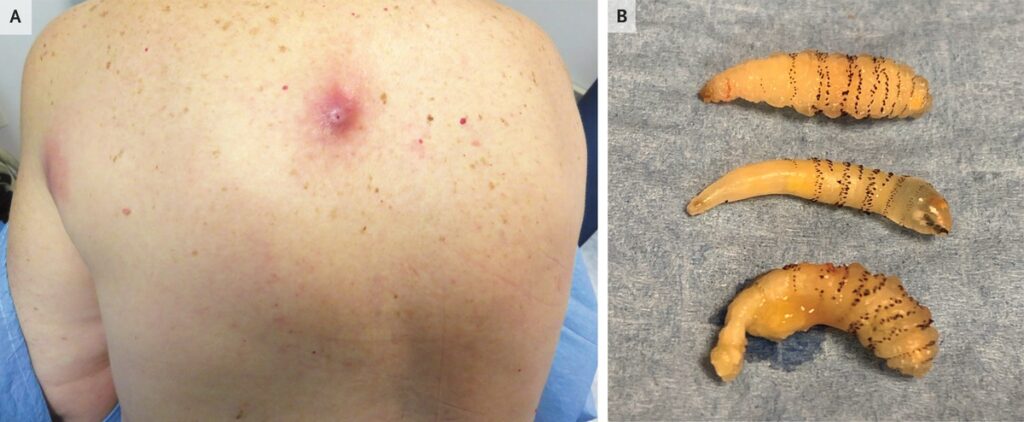
To prevent botfly infestations, regular grooming of pets and cattle, wearing protective clothing such as long sleeves and pants when in botfly-prone areas, using insect repellents designed to repel botflies, and maintaining a clean environment are all recommended precautions.
Botflies, with their unique life cycle, offer a fascinating but unwelcome presence. Understanding their biology, removal techniques, and prevention strategies is crucial for minimizing the discomfort and health risks associated with these parasitic insects. In case of an infestation, seeking professional help is advised to ensure safe and effective removal.


